
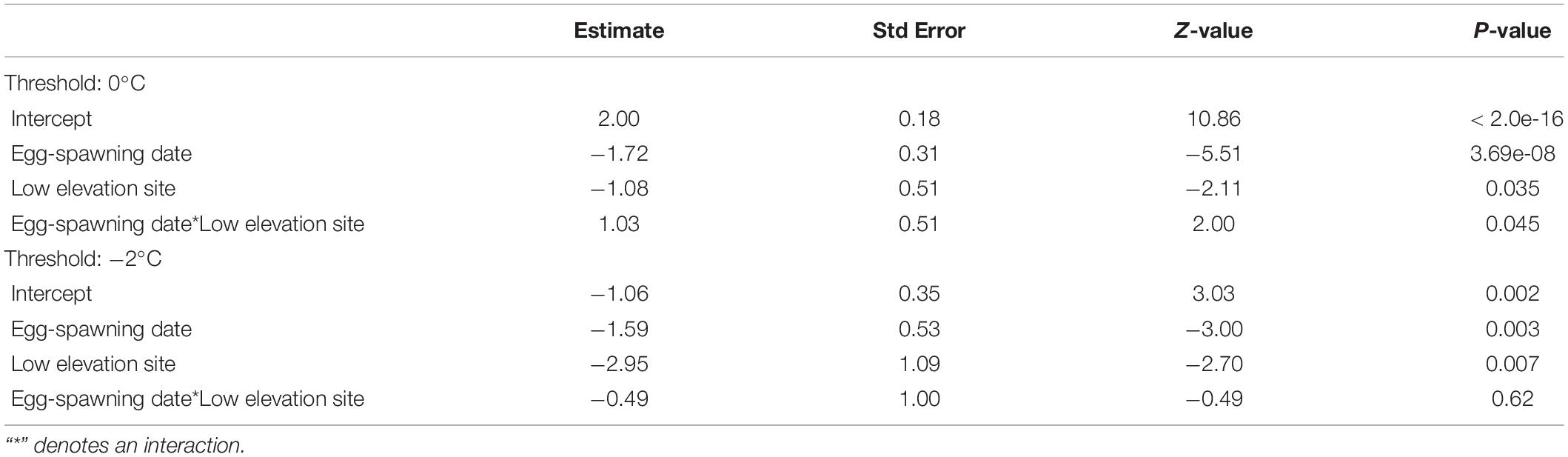
The reference genome sequence and annotation files were downloaded from ENSEMBL, release.92 (Mus_musculus.GRCm38.92.fa, and Mus_musculus.GRCm38.92.gtf). Statistical analysis of differentially expressed genes is carried out based on a negative binomial model using a tool in CLC Genomic Workbench. The aligned reads were obtained using the RNA-Seq Analysis Tool of CLC Genomics Workbench. The reference genome sequence and annotation files were downloaded from ENSEMBLE, release.92 (Mus_musculus.GRCm38.92.fa, and Mus_musculus.GRCm38.92.gtf). Bases with low quality were trimmed and reads are mapped to reference genome Mus musculus genome GRCm38. De-multiplexed fastq files from RNA-Seq libraries are imported into the CLC software. CLC Genomics Workbench 11.0.1 version ( Qiagen) was used for RNA-seq analysis. The sequencing of the cDNA libraries was performed on the Illumina NextSeq platform (Illumina, San Diego, CA) using the high output 1X75 cycles configuration. Methods: Illumina compatible RNAseq library was prepared using NEB next ultra RNAseq library preparation kit. The goals of this study are to compare NGS-derived brain transcriptome profiling (RNA-seq) to reveal the difference of cellular pathways in adult brains of wild type (WT) and monocyte-depleted (CCR2-DTR) mice 8 days post infection of Trichinella spiralis. Purpose: Next-generation sequencing (NGS) has revolutionized systems-based analysis of cellular pathways. Next-Generation Sequencing Facilitates Quantitative Analysis of Wild Type and Monocyte-Depleted Brain TranscriptomesĮxpression profiling by high throughput sequencing GEO help: Mouse over screen elements for information.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
